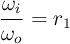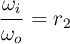Example 2: Gear Shift (2)
- Mathematical problem:
- event at gear shift r1 → r2
- rotational speeds before event
- rotational speeds after event
- start values of ωi, ωo after
event undefined
- simple solution
- fix one ω and compute the other
- → often unrealistic behaviour
- Reality check:
- problem appears in reality as well!
- modern transmissions use synchronizer rings
- adapt rotational speeds using friction
- basically simple clutches
- ω's adapt dynamically (according to connected
inertias)
- Extended Model:
- new gear shift model
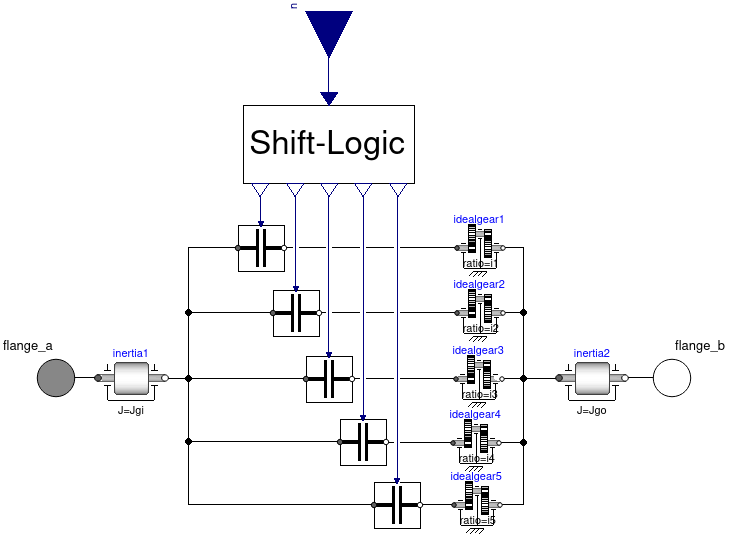
- one clutch per gear
- shift logic component
- detects gear change and opens/closes
corresponding clutches
- clutch of current gear is closed
- other clutches are open
- works with one new parameter for shifting time