-
- The power of a computer is its versatility: It can be programmed, i.e. its
basic commands can be combined to do very different tasks.
- Typical basic commands:
- data movement
- ``get data from memory cell 4228 into register r3''
- computation
- ``add content of registers r1 and r2 and store the sum in r3''
- program flow
- ``get the next command from memory cell 2001, if register r1 contains 0''
- Program: a sequence of commands that can be executed by a computer.

- The set of basic commands that a computer understands, forms a special
programming language, the machine language. It is different for
different kinds of computers.
-

- Programming in machine language requires a thorough understanding of
the internal structure of the used computer (registers, built-in
arithmetic and logical units etc.). It is hard to write such a
program to solve a real problem.

- ``Real'' problems could be
- -
- Compute the approximate value of an integral of a special function between
given bounds.
- -
- Interpret the given human sentence to find out what kind of request is
made at the hotel reservation system.
- -
- Find all the persons in a large set of banking account data, whose account
is overdrawn by a certain amount.

- To make the task of programming computers simpler, many programming
languages have been invented that use higher abstractions from the
particular application area.

- Some specialized programming languages:
- -
- Mathematical abstractions are the realm of Fortran. It understands
a mathematical formula like
in the following simple form:
x1 = -p/2 + sqrt(p**2/4 - q)
- -
- Logical dependencies and relations are the basic commands of
Prolog. It allows to formulate things like
Sentence =
(Subject phrase + Verb phrase) OR
(Subject phrase + Verb phrase + Object Phrase)
- -
- Special database languages like SQL allow direct queries in the
data, e.g.
Show all NAME fields
in data set ACCOUNTS
where (AMOUNT < -100 Euro)

- Programms written in such languages have to be translated into machine
language, before they can be executed on a computer. This - rather tedious -
task can itself be delegated to a computer program.
Compiler: a program that reads a program text as input and translates
it into machine language.

- A class of very popular programming languages are the object oriented
languages. They allow to construct programs from smaller building blocks
(the objects), which contain a certain amount of information and
have a given behaviour.

- An object consists of fields that contain the object's data, and of
methods, which describe its possible actions.

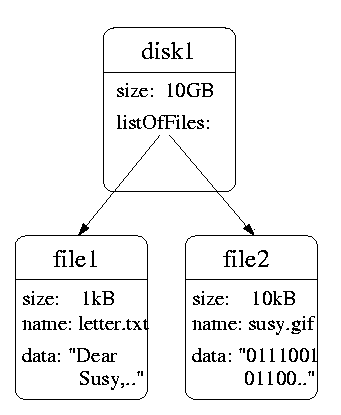
- An operating system could organize the data on a disk using objects like
File
fields: size, name, data
methods: getSize, appendData(newData)
Disk
fields: size, listOfFiles
methods: createNewFile(name), getFreeSpace

- A class is the description of all objects that have the same kind of
data fields and the same methods.

- The objects file1 and file2 belong to the common class File.

Peter Junglas 8.3.2000
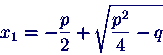
![]()