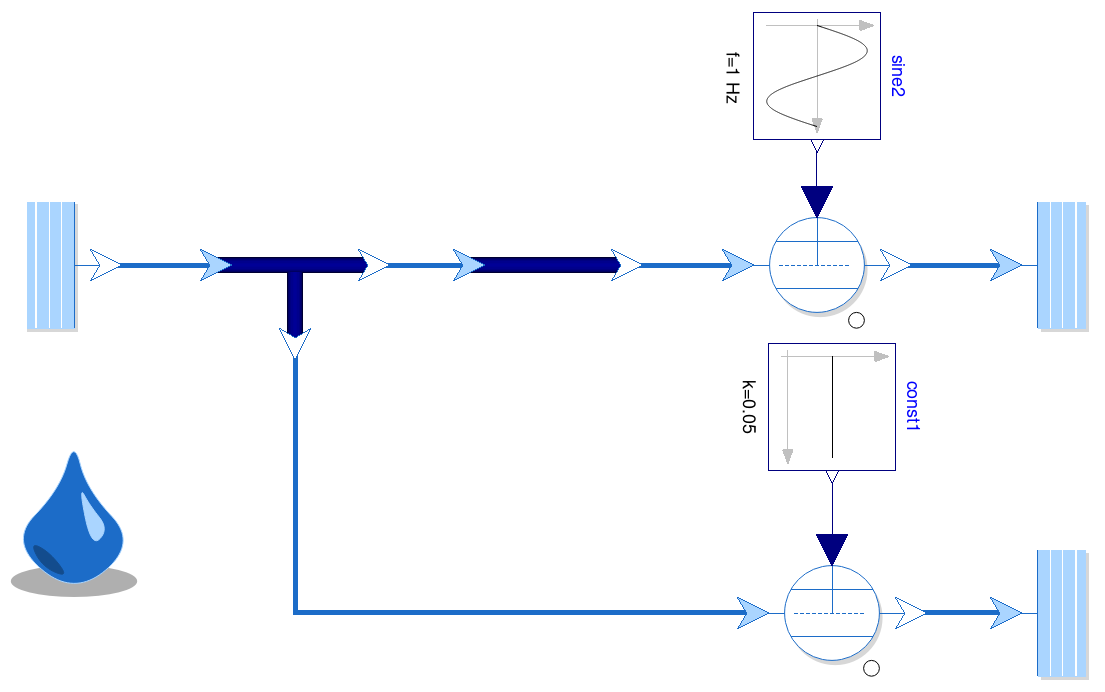
Example 4: Distribution of compressed air (1)
- Basic system:
- simple pneumatic system with pressure source, tee
branch, pipe and consumers
- Model in Modelica:
- uses PneuBib library
- PneuBib itself based on MSL Fluid library
- MSL Fluid library basically describes quasistatic
processes
- run in Dymola →
- Failed to solve nonlinear system using
Newton solver...
At time T = 5.130275e-04
...
the corrector could not converge ...
Integration will be terminated.
- Mathematical problem:
- model consists of 170 equations, many are coupled and
highly non-linear
- proper initial values are unknown and guessed by
solver
- → Newton solver does not converge
- well-known problem of MSL Fluid library
- Reality check:
- system starts with ambient pressure and zero mass
flow everywhere
- switching on pumps etc.
- → global pressure difference increases
- → mass flows increase slowly due to mass inertia
- → local pressure differences build up